Key takeaways
- OpenStreetMap provides free, community-driven mapping data with global coverage.
- Address search maps require API keys and proper error handling implementation.
- Leaflet.js provides light-weight JavaScript library for creating interactive web maps.
- Regional coverage variations and data quality considerations make provider selection important for global applications.
Finding addresses and places on maps is something we do almost daily. Whether you’re building a web application or just need to locate a specific address, OpenStreetMap (OSM) offers a robust, open-source solution.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about implementing address search functionality using OpenStreetMap.
Introduction to OpenStreetMap
OpenStreetMap (OSM), often called the “Wikipedia of maps,” is built by volunteers who contribute roads, buildings, landmarks, and even postal codes to its database. This global effort creates a free, detailed map that developers widely use.
OSM provides geocoding and reverse geocoding capabilities through various tools and APIs. The most notable is Nominatim, which converts addresses into geographic coordinates and vice versa. It’s the engine behind the search box at nominatim.openstreetmap.org.
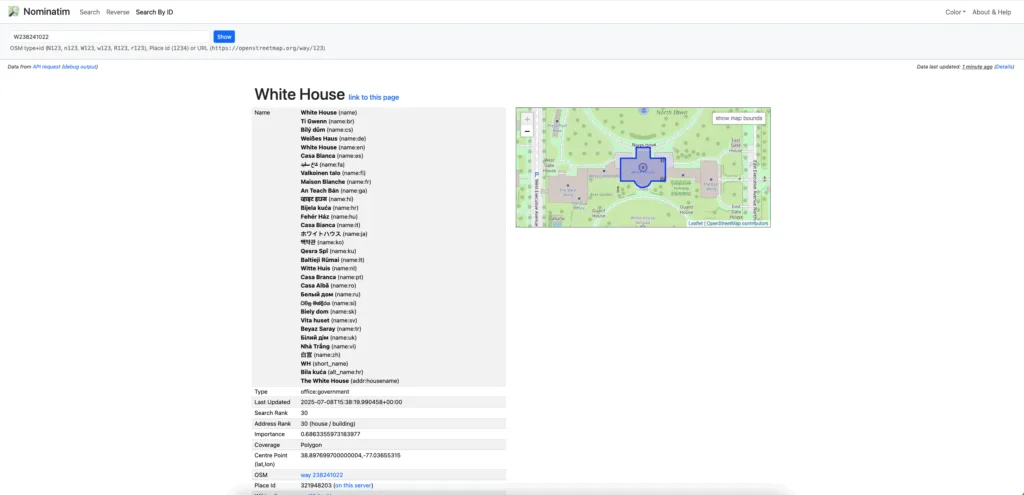
For now, let’s begin with a step-by-step guide to implementing the address search function with OpenStreetMap.
Step 1: Create a Basic Map
Before adding an address search, you need to establish a foundation with a basic map. In your project directory, set up an index.html and script.js. The easiest way to add a basic map with OpenStreetMap is by using Leaflet.js, a lightweight JavaScript library for interactive maps that works well across different devices and browsers.
First, include the Leaflet CSS and JavaScript files in your HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="<https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/leaflet.css>" />
<style>
#map { height: 400px; width: 100%; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map"></div>
<script src="<https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/leaflet.js>"></script>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Now, in the script.js file, initialize your basic map with a few lines of JavaScript:
// Initialize the map
const map = L.map('map').setView([51.505, -0.09], 13);
// Add OpenStreetMap tile layer
L.tileLayer('https://{s}.tile.openstreetmap.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png', {
attribution: '© OpenStreetMap contributors'
}).addTo(map);
Your map will show zoom controls, attribution, and tile layers from OSM servers. It’s a solid starting point for displaying geographic data, and we’ll build on it with search features in the next steps.
Step 2: Add Address Autocomplete Plugin
With your basic map ready, the next step is adding an address search. A popular choice is the Leaflet Geoapify Address Search plugin, which provides real-time autocomplete as users type, resulting in a smooth and user-friendly experience.
You have two main installation options for adding the plugin. If you’re using NPM for modern JavaScript projects:
npm i @geoapify/leaflet-address-search-plugin
Or you can link directly to the CDN for simpler implementations:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="<https://unpkg.com/@geoapify/leaflet-address-search-plugin@^1/dist/L.Control.GeoapifyAddressSearch.min.css>" /> <script src="<https://unpkg.com/@geoapify/leaflet-address-search-plugin@^1/dist/L.Control.GeoapifyAddressSearch.min.js>"></script>
It handles complex tasks, such as formatting queries, communicating with the API, and displaying results. You can also customize its style, filters, and behavior to fit your needs.
Step 3: Get an API Key
Most address search tools need an API key for access, even for free use. It helps control traffic and prevent misuse. For Geoapify, sign up at myprojects.geoapify.com to get your key instantly.
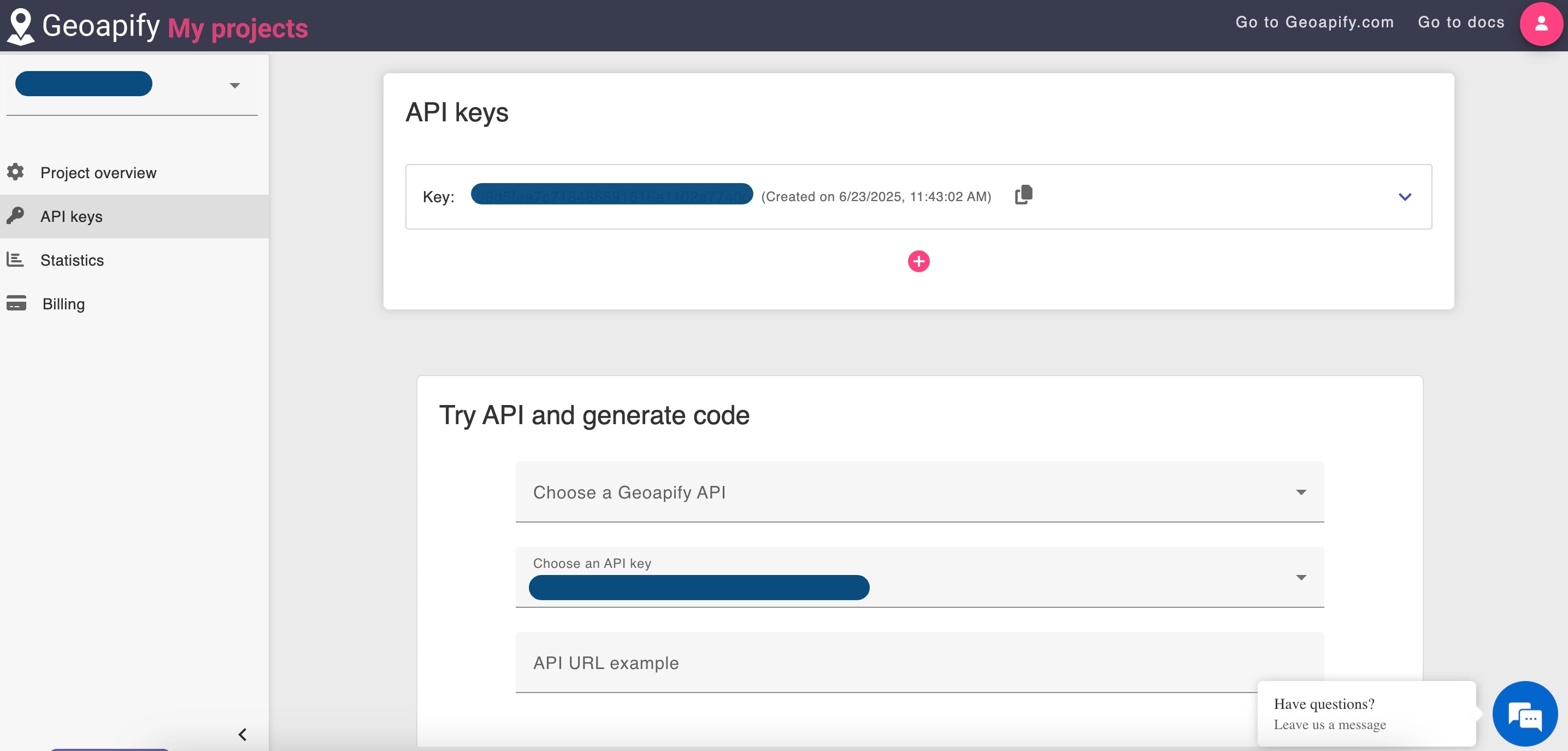
Free plans usually give you around request limits (3,000 per day), which is enough for testing and small projects. But if you need higher limits, paid plans offer expanded quotas and additional features.
Keep your API key secure. Avoid exposing it in public code; use environment variables or server-side proxies instead. Some services also let you limit your key to specific domains for added security.
Step 4: Add an Address Search Field to the Map
Now that you have your API key, you can add the search feature to your map. The address search control integrates seamlessly into Leaflet’s system, allowing you to place and style it like any other control. Here’s how to create and add the search control to your map:
In your script.js file:
// Your API key from Geoapify
const apiKey = 'your-geoapify-api-key-here';
// Create the address search control
const addressSearchControl = L.control.addressSearch(apiKey, {
position: 'topleft',
resultCallback: (address) => {
console.log('Selected address:', address);
},
suggestionsCallback: (suggestions) => {
console.log('Available suggestions:', suggestions);
}
});
// Add the control to the map
map.addControl(addressSearchControl);
For more advanced configurations, you can specify additional options:
const addressSearchControl = L.control.addressSearch(apiKey, {
position: 'topleft',
placeholder: 'Enter address here...',
maxSuggestions: 5,
debounceDelay: 300,
countryCodes: ['US', 'CA', 'GB'], // Limit to specific countries
resultCallback: (address) => {
// Handle address selection
map.setView([address.lat, address.lon], 16);
L.marker([address.lat, address.lon]).addTo(map)
.bindPopup(address.display_name)
.openPopup();
}
});
The search control handles everything—keyboard input, clicking, and highlighting results. When someone picks an address, the map smoothly zooms to that spot, giving instant visual feedback.
Best Practices for Implementation
To achieve the best results from OpenStreetMap address searches, it’s essential to follow a few key best practices. Begin with comprehensive error handling to deal with API failures, network issues, or unexpected data formats gracefully:
// Error handling example
async function safeGeocode(address) {
try {
const response = await fetch(`https://nominatim.openstreetmap.org/search?format=json&q=${encodeURIComponent(address)}`);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
const data = await response.json();
return data.length > 0 ? data[0] : null;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Geocoding failed:', error);
// Show user-friendly error message
alert('Address search temporarily unavailable. Please try again later.');
return null;
}
}
Implement appropriate caching strategies to reduce API calls and improve response times:
// Simple caching implementation
const geocodeCache = new Map();
async function cachedGeocode(address) {
const cacheKey = address.toLowerCase().trim();
if (geocodeCache.has(cacheKey)) {
return geocodeCache.get(cacheKey);
}
const result = await safeGeocode(address);
if (result) {
geocodeCache.set(cacheKey, result);
}
return result;
}
Add fallback options in case your primary search services fail. Using multiple data sources or providers helps keep your app running smoothly, even when one service experiences issues.
Strengths of OpenStreetMap
OpenStreetMap offers several notable advantages for developers and organizations:
- Cost-effective solution: Provides completely free access to global mapping data without licensing fees or usage restrictions, making it valuable for educational projects, non-profits, and startups with limited budgets.
- Complete customization control: The open-source nature allows developers to customize and extend the data according to their specific needs without vendor lock-in concerns.
- Community-driven updates: An active community continuously updates and improves the data, with local contributors frequently adding detailed hyperlocal information that reflects real-world changes quickly.
- Synthetic addresses generation: OSM creates estimated addresses by inferring location data from nearby map features when complete address information isn’t available. For example, if a building exists on a street but lacks a specific house number, OSM might generate an approximate address based on the building’s position between known addresses. This interpolation helps fill gaps in search results.
Drawbacks of OpenStreetMap
Despite its advantages, OpenStreetMap comes with certain limitations that you should consider carefully. While the community-driven approach generates vast amounts of geographic data, it also introduces several challenges that can impact business applications and user experiences.
Understanding these potential drawbacks helps you make informed decisions about whether OSM meets your project requirements. Here are the key limitations to consider:
- Unreliable Synthetic Addresses: While the synthetic address generation approach of OSM helps improve search functionality, these inferred addresses can be inaccurate or misleading, making them unsuitable for applications that require verified, authoritative address data—such as shipping, compliance, or location-based billing.
- Data Inconsistency and Vandalism Risks: OSM’s open-edit model means anyone can alter your location data, creating reliability risks for business operations. The Pokémon Go incident proved this vulnerability—users manipulated map data for gaming purposes, compromising data integrity for legitimate applications.
- Inconsistent Data Quality: OSM coverage varies dramatically by region—Western Europe offers detailed mapping while developing markets often lack comprehensive data. This inconsistency becomes problematic when your business operates globally or expands into new territories.
- Time-Consuming Data Processing: Raw OSM data isn’t always clean or standardized, making it difficult for companies to process automatically or meet their specific needs. Consequently, additional work, such as validation and enrichment, is often required, adding time and cost.
- Commercial Licensing and Legal Issues: It is important to note that open-source data does not mean you may use it for everything. Each dataset is available through specific license terms, indicating what use of the data is permitted. It is critical that you check the license before working with the data.
💡 Struggling with OpenStreetMap’s data inconsistencies? GeoPostcodes’ ZIP code and address databases cover 247 countries with standardized, accurate data, curated from 1,500 authoritative sources. Trusted by Amazon, DHL, and 124 Fortune 500 companies to scale their global operations. Request a quote here.
Conclusion
OpenStreetMap is a flexible, open-source option for adding address search to web applications. With global coverage and strong community support, it’s a good fit for small projects. While some technical setup is needed, tools like Leaflet.js and search plugins make implementation straightforward.
However, for businesses requiring consistent global coverage, standardized formats, and reliable support, professional location databases often offer better long-term value than OSM.
Providers like GeoPostcodes can overcome the limitations of open-source data by delivering accurate, standardized reference data from over 1,500 sources for 247 countries. With over 15 years of experience, we guide your implementation and solve your technical challenges. We invite you to Browse our databases for free or request a quote here.
FAQ
Does OpenStreetMap have addresses?
Yes, OpenStreetMap address search contains full address data from OSM objects.
Each entry includes latitude, longitude coordinates.
However, completeness varies and bug reports help improve documentation quality.
How do I get an OpenStreetMap?
You can access OpenStreetMap data by visiting the main website or checking the documentation for download options. Use geocoding software to perform address searches and location queries. Coverage tends to be most comprehensive in regions with Latin-based writing systems.
Is there an open source street view?
Yes, several open-source projects provide street-level imagery that can be integrated with web mapping applications. These alternatives offer varying levels of coverage and image quality depending on the region. Popular options include Mapillary and KartaView, which rely on community-contributed photos to create street-level views.
How do I find a street address on a map?
You can search for addresses using geocoding services that convert text addresses into map coordinates. Most mapping applications include a search box where you can enter an address and receive location results. The process typically involves typing the address, selecting from suggested results, and viewing the location on the map with optional markers or popups.
What alternatives exist to OpenStreetMap for address data?
GeoPostcodes offers a comprehensive global address validation database that provides more structured and validated address data compared to crowd-sourced alternatives.
Our world postal code database includes verified addressing information.
How can I access a master list of addresses?
GeoPostcodes provides a master address list that includes comprehensive address data for various regions, particularly detailed US addressing information.