Key Takeaways
- Customer movement analysis using polygons reveals patterns that optimize layouts, promotions, and service strategies.
- Competitor tracking within defined polygons identifies market gaps, helping businesses refine expansion and positioning plans.
- Points of interest (POI) and indoor mapping uncover deeper audience behaviors, boosting location-based strategies.
Introduction
Have you ever noticed how some businesses effortlessly reach the right customers at the right time? That’s the power of geomarketing. Instead of broad targeting, it uses accurate location data to connect with people based on their location.
Geomarketing combines location and marketing data to find better spots and reach customers. It uses accurate polygons instead of simple radius targeting.
This distinction matters: real-world geography isn’t made of perfect circles. Neighbourhoods and districts have irregular shapes, and polygon geomarketing allows businesses to target them precisely.
Why Polygon Geomarketing?
Geomarketing offers significant advantages over traditional radius targeting by providing more precise and strategic location-based marketing capabilities.
Radius targeting draws a simple circle around a point. Geomarketing, by contrast, uses custom polygon shapes that reflect real-world geography—neighborhood lines, shopping habits, competitor sites, and barriers like rivers or highways.
- Geographic definition: Polygon geomarketing uses multi-sided shapes that match real-world boundaries like zip codes, business districts, or specific neighborhoods.
- Precision: Polygon geomarketing targets the exact zip codes where your best customers live. It helps you make every marketing dollar count.
💡Get administrative and zip code polygons for 247 countries, including difficult geographies such as China, the UK, Russia, or Brazil. Try our boundaries database for free.
- Flexibility and real-world alignment: With polygon geomarketing, you define territories using real boundaries, behavior, or goals. Marketing aligns with geography, not vague shapes.
- Resource efficiency: Polygon geomarketing reduces waste of resources, such as time and money, by targeting areas with concentrated customers.
| FEATURE | TRADITIONAL RADIUS TARGETING | POLYGON GEOMARKETING |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Definition | Uses simple circles around points | Uses actual geographic boundaries (zip codes, neighborhoods) |
| Precision | Low – includes irrelevant areas | High – matches real-world boundaries |
| Flexibility | Limited to circular areas | Can target irregular shapes and specific territories |
| Resource Efficiency | Often wastes marketing budget on irrelevant areas | Focuses resources on precisely defined relevant areas |
| Real-World Alignment | Ignores natural boundaries like rivers, highways | Respects actual geographic divisions and barriers |
Location Intelligence: The Foundation of Smart Geomarketing
Location intelligence is the secret behind effective polygon geomarketing. It’s what transforms those dry coordinates and boundary lines into goldmines of business insight.
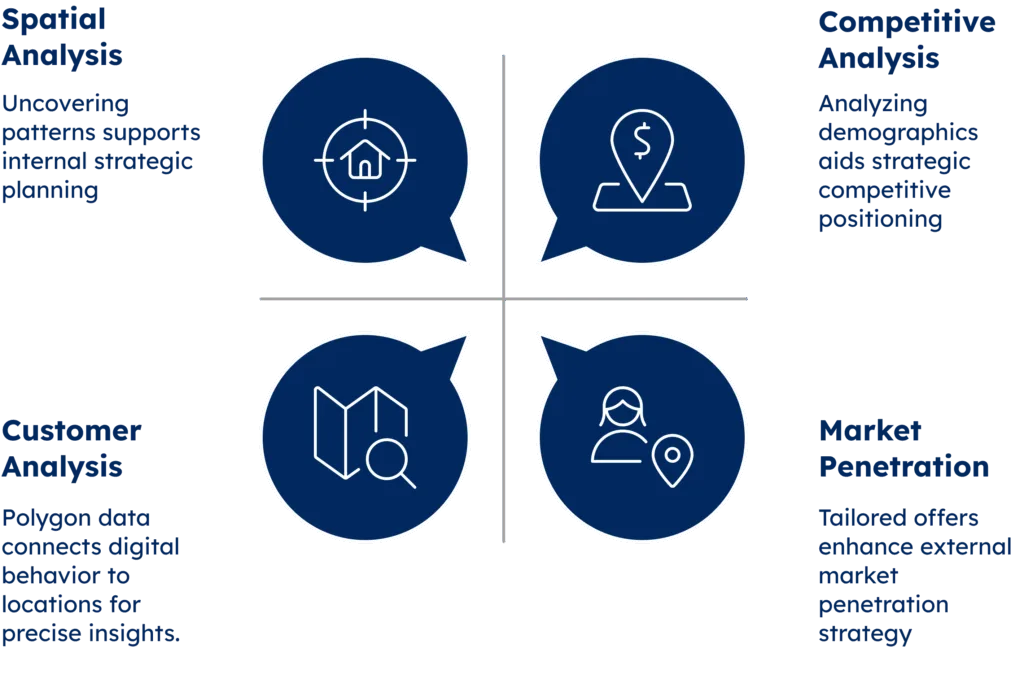
Now, let’s talk about key features. What are the main components of location intelligence, and how does polygon data fit into the picture?
- Spatial analysis: Location intelligence combines geographic and business data to find hidden patterns. It shows businesses where their customers are and where to grow.
- Competitive analysis: Polygon-based insights help businesses find accurate zip codes. They reveal where ideal customers live and where competition is low.
💡Discover our worldwide administrative and zip code boundaries. Our boundary data can be enriched with country-specific information, population, and multi-language support. Unlock all countries for free.
- Market Penetration: Businesses can deliver personalized offers as prospects enter defined business districts. The result is timely, relevant outreach.
- Customer Analysis: Polygon data improves customer mapping with precise boundaries. It connects digital behavior to real-world movement, helping drive local, data-based decisions.
The image below summarizes the main features of location intelligence.
Polygon Geomarketing and Audience Targeting: Know Your Customers
In marketing, knowing your audience is vital. Polygon geomarketing reveals detailed area profiles. It highlights changing client needs in places like financial districts and industrial hubs.
This level of detail is game-changing—tracking how clients find you, engage with your offerings, and what they buy. Mapped to specific territories, whether a city in Mexico or Japan, these insights uncover patterns that can redefine sales strategies and product development.
Its ability to connect digital behavior with physical location makes this approach powerful. Combining online research with workplace geography gives you a clear view of a prospect’s needs. That makes outreach more relevant and less generic.
Mobility Analysis: Understanding Customer Movement
How clients move through physical spaces is the key to understanding their needs and behaviors. Mobility analysis with polygon data uncovers these patterns, turning movement into actionable insights. Let’s discover relevant metrics of mobility analysis.
- Foot Traffic: Polygon data tracks movement with precision. It reveals peak zones and times to guide smarter choices on store hours and locations.
- Dwell Time: Mapped to polygon boundaries, time spent in locations shows where clients linger. This helps B2B and B2C providers find high-interest districts and understand why.
- Entry Points: Movement patterns reveal how customers enter and move through areas. This helps improve layouts, signage, and services for better engagement.
- Traffic Flow: Polygon data shows how people move through an area. This helps businesses design spaces that match natural movement patterns.
- Seasonal Patterns: Polygon-based tracking shows how movement shifts over time. This helps optimize staffing, inventory, and seasonal promotions.
| METRIC | WHAT IT MEASURES | BUSINESS APPLICATION |
|---|---|---|
| Foot Traffic | Volume of visitors across polygon areas | Store location optimization and staffing decisions |
| Dwell time | How long customers stay in specific locations | Store layout improvements, engagement strategies |
| Entry points | How customers enter defined areas | Signage placement, store design optimization |
| Traffic flow | Movement patterns within and between polygons | Product placement, store layout planning |
| Behavioral Analysis | How mobility changes across different time periods | Seasonal marketing planning, inventory management |
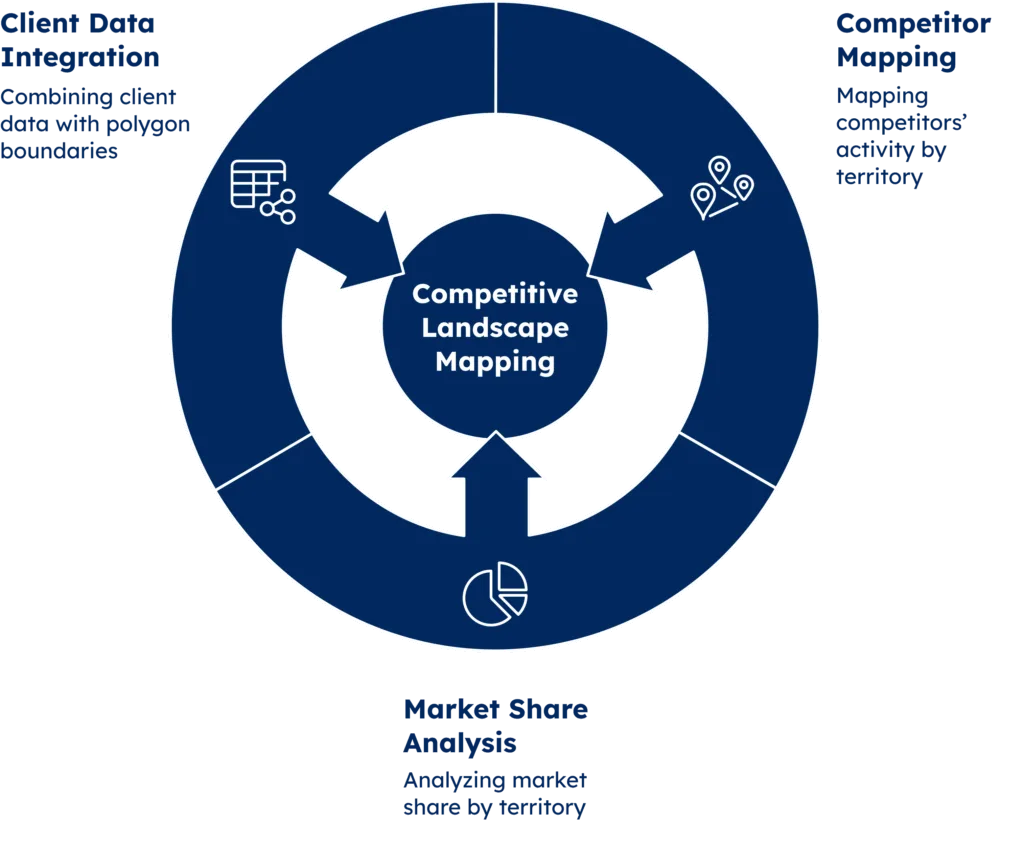
Competitor Tracking: Mapping the Competitive Landscape
Tracking your competition is essential. Polygon geomarketing gives you accurate tools to map competitor activity by territory. This helps you build strategies that strike where it matters most.
Polygon data shows exactly where competitors are active, revealing coverage patterns and gaps. A global provider might see a rival dominating some districts. But nearby zones may be ignored, creating clear chances to expand.
More than just maps, polygon competitor analysis clearly shows market share by area. You’ll see where you lead, where rivals dominate, and where the fight is still open, enabling finely tuned responses for each market.
Client data mapped to polygon boundaries reveals which competitors attract key segments. Use it to fine-tune your positioning and grow market share.
The image below summarises how polygon geomarketing maps the competition.
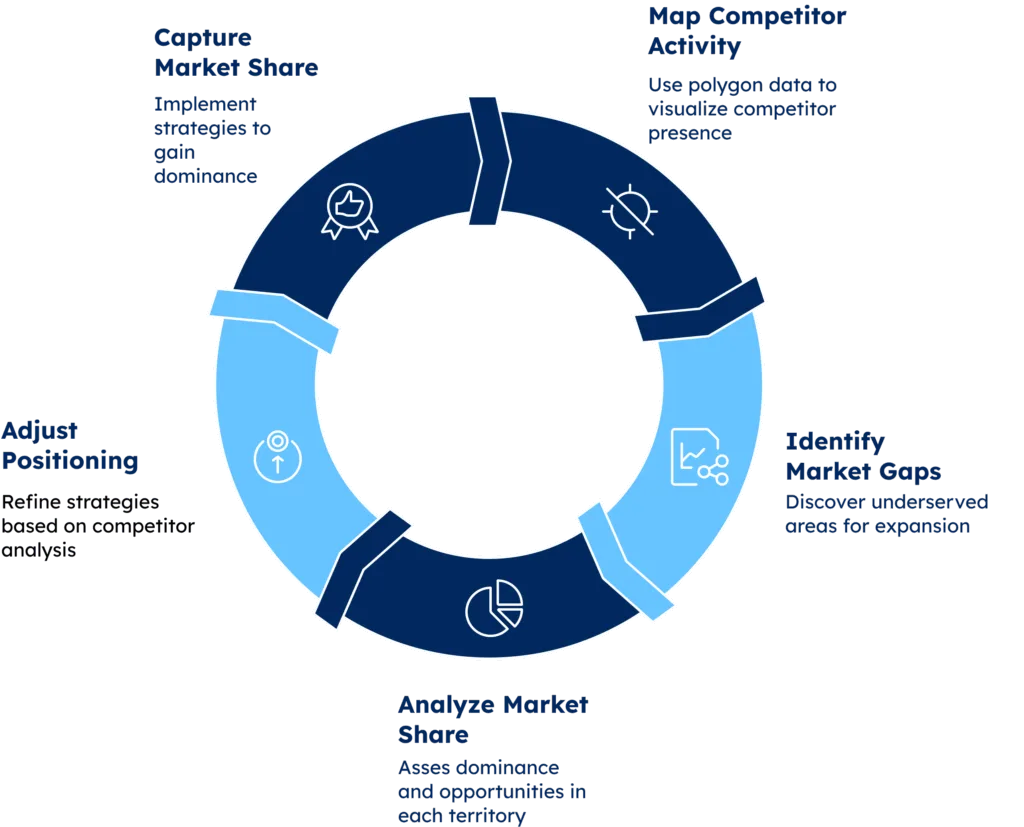
Strategic Application of Competitor Intelligence
Strategic application of competitor intelligence involves systematically gathering, analyzing, and leveraging data about rival businesses to inform critical decision-making across all levels of an organization.
By understanding competitors’ pricing strategies, market positioning, product offerings, operational strengths, and weaknesses, companies can identify untapped market opportunities, anticipate industry trends, and develop more effective competitive strategies.
This intelligence enables businesses to benchmark their performance, adjust their value propositions, optimize resource allocation, and make proactive moves rather than reactive responses.
When applied strategically, competitor intelligence becomes a powerful tool for differentiating brand positioning, capturing greater market share, and maintaining sustainable competitive advantages in increasingly crowded marketplaces.
The image below highlights the key benefits of using competitor intelligence strategically.
Points of Interest: Creating Meaningful Connections
- Retail Locations: Polygon data maps key points of interest—like HQs, logistics hubs, and business centers. It reveals commercial density, shows the competition, and guides better site selection.
- Entertainment Venues: Understanding lifestyle habits near business districts shows why certain venues thrive. This insight makes expansion planning more strategic.
- Public Services: Each polygon includes a mix of business types—financial, industrial, or commercial. This combination shapes client habits and needs. Use it to match your services to the pace of each area.
- Landmarks: Track how professionals move between landmarks in set zones. This helps align your operations and messaging with natural business flow.
Define Metropolitan Areas: Scaling Your Strategy
Metro zones hold high concentrations of business activity, talent, and growth potential. Polygon data helps you tap into these areas with precision. What makes metro analysis valuable? Let’s break down its key components and strategic benefits.
- Precise Definition: Polygon data breaks metro areas into clear business zones based on density, borders, and economic trends. This reflects real activity, not vague regions.
- Cross-Market Comparison: With precise boundaries, businesses can compare metro markets. They can study client behavior and performance by zone to find patterns and new opportunities.
- Strategic Consistency: Professional services firms can grow internationally with smarter decisions. This helps decide what to standardize globally and what to tailor locally.
- Urban Dynamics: Polygon data shows how city centers and outer areas behave across regions. Downtown patterns often differ between Asian and European cities.
- Operational Optimization: Polygon mapping improves decision-making. It guides supply chains, service areas, and delivery zones. It adapts to each city’s layout and transit flow.
- Communication Flow: Tracking influence across urban areas helps shape sharper outreach and thought leadership strategies.
The image below highlights key points of the strategic value of metropolitan area analysis using polygon data.
Conclusion: Leveraging the Power of Polygon Geomarketing
Polygon geomarketing takes raw location data and turns it into strategy. It powers smarter targeting, reveals competitor moves, and unlocks growth zones.
For more than fifteen years, GeoPostcodes location data experts have provided verified datasets that power top-tier geomarketing. Download a free sample.
FAQ
How does advertising polygon data help?
Advertising polygon data helps by allowing businesses to create a virtual boundary around specific locations, targeting potential customers based on their real-world movements.
What is polygon data geomarketing?
Polygon data geomarketing uses precise geographic shapes instead of a simple bounding box to define areas, making it easier to send push notifications or text message alerts when a phone entering a targeted space is detected.
How does a user’s mobile device interact with a polygon?
A user’s mobile device can trigger app based push notifications or text message alerts when it crosses an entry point captured within a polygon, such as parking lots near a food outlet.
What is an example of targeting a hungry and pressed customer?
When a hungry and pressed customer is within a few miles of a marked store like McAlister’s Deli, businesses can send push notifications with a compelling offer to prompt immediate visits.
What kind of output can be generated from polygon data?
Polygon data can generate a polygon screenshot, a text file, or another form of output that helps businesses understand object movements in many different contexts, making data-driven marketing strategies more effective.
What is a polygon in geolocation and how does it help with advertising?
A polygon in geolocation is a defined area on a map, typically created using GPS coordinates, that marketers use to target specific locations for advertising.
By setting precise boundaries, businesses can deliver ads to users within those areas, enhancing the relevance and effectiveness of their campaigns.
How does polygon data improve geomarketing strategies?
Polygon data allows businesses to create custom-shaped target zones, enabling hyper-local advertising.
This precision helps in reaching the right audience, measuring foot traffic, and analyzing the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
What is polygon segmentation and why is it useful for target audiences?
Polygon segmentation involves dividing a geographic area into smaller, more precise zones using polygons.
This segmentation allows advertisers to tailor their messages to specific subgroups within a larger audience, improving the relevance and effectiveness of their campaigns.
What is the difference between a polygon and a bounding box in geolocation?
A polygon is a custom-defined area with specific boundaries, allowing for precise targeting.
A bounding box, on the other hand, is a rectangular area defined by two opposite corners, offering less precision than polygons.