Global Address Validation for
ISO 20022 Compliance
Transform your global addresses into ISO 20022 compliant
formats without disrupting your operations.


ISO 20022-ready data
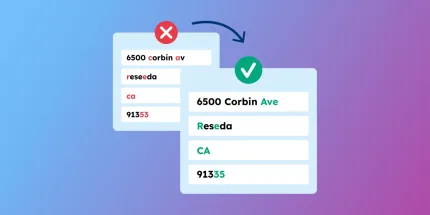
Reliable ZIP codes & address formats to ensure full ISO 20022 compliance. Accurate and up-to-date.
Standardized structure
Unified global structure with standardized fields, multi-language, and consistent administrative levels.
Self-hosted database
Enhanced security, compliance, and performance at a fixed cost, no matter the volume.
Trusted address validation
Keep your addresses validated and always complete with ZIP code, city and street data. Ensure they are correctly mapped into the new ISO 20022 format.
The challenges of ISO 20022 compliance
sources
addresses
formats
Make your address data ISO 20022-ready
Reliable reference data
Our advanced data pipelines capture, clean, format, and integrate new data consistently.
Our long-standing partnerships with national and international postal operators, such as USPS, guarantee the timely delivery of accurate information.
1,500 verified data sources
Multi-language support
Our address formats cover all official address names in the official local languages, foreign names, English, and transliterations into the Roman alphabet.
299 languages available
Address compliance experts
Our team of experts provides support and expert guidance to ensure your address data is structured and compliant with global ISO 20022 requirements.
Our guide for ISO 20022 address compliance
What is the ISO 20022 address format, and what are the new specifications? Our guide breaks down the complexities and helps you map your existing address data to the new standards for full compliance.

Trusted by Industry Leaders
Join more than 100 enterprise clients who trust GeoPostcodes for their location data
Anjo Grebe
Consultant


Dr. Peter Wild
Managing Partner

Kousha Mazloumi
Director of Data Science

Kousha Mazloumi
Director of Data Science

William Chao
Product Owner of Geographic Information Services


Kate Kilby
Senior Product Manager

Dave Hamm
Project Manager

Kavian Ranjbar
Data Governance Specialist

Nick Beaugié
Senior Software Engineer
Why choose GeoPostcodes
Global coverage
Complete coverage across 247 countries, including hard-to-source geographies like China, Japan, Brazil, and Russia.
Highest quality
Built on extensive, authoritative sourcing with robust data engineering and quality control. Standardized and up-to-date.
Expert Consulting
With 15 years of experience, we guide your implementation and deliver data in the format that fits your system.
Our selection on address data compliance
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 20022 is a global financial messaging standard used by major financial institutions to improve data quality in international financial transactions. The standard requires every field—especially address format and postal addresses—to follow strict rules. Because unstructured addresses frequently cause errors, proper ISO 20022 address validation ensures each record uses clean, predictable address data and a valid country code.
To understand how global address structures differ, see International Address Formats Explained.
To convert existing address data into a compliant structure, financial institutions must replace unstructured addresses with structured address formats. This includes normalizing components such as street lines, postal addresses, regions, and the required country code. Many organizations transition through a hybrid format when legacy systems contain mixed or inconsistent address rules. Correct mapping and cleansing ensures full ISO 20022 compatibility.
For guidance on cleaning and standardizing address components, see Address Standardization: Benefits and Methods.
Cross-border postal addresses often use different field conventions, making compliance difficult. Many regions rely heavily on unstructured address data, which creates issues for financial institutions that must meet ISO 20022 requirements. Missing country codes, inconsistent structures, and fragmented address fields lead to message rejections. Converting unstructured inputs into clear, structured formats is essential to avoid compliance failures.
For an overview of how address structures vary globally, see ZIP Code vs Postcode: Key Differences Worldwide.
Global payment systems operated by major financial institutions—including those supporting cross-border payments—now mandate ISO 20022 to improve interoperability and reduce errors. These systems depend on strict address format definitions, standardized postal addresses, and complete, structured fields. As global adoption expands, institutions using unstructured or inconsistent formats will face growing compliance pressure.
To understand the importance of consistent international identifiers, see International Address Formats Explained.
Multilingual address data can easily become unstructured if formatting rules aren’t enforced. When multiple languages or scripts appear in a hybrid address field, institutions struggle to validate them under ISO 20022. Ensuring a consistent country code, converting postal addresses into structured fields, and standardizing the format helps prevent validation failures caused by unstructured data.
For more on managing global address variability, see Address Standardization: Benefits and Methods.
ISO 20022 requires each address line to follow a clear, predictable structure. Unstructured lines frequently trigger validation errors. When organizations convert legacy address content into a standardized line format, they reduce ambiguities and improve message quality for financial transactions. Consistent address line usage ensures compatibility with global payment networks.
To learn how different countries structure address lines, see International Address Formats Explained.
A uniform, structured format ensures every address line follows the same predictable pattern. This eliminates problems caused by unstructured data, improves automation, and enables cross-border payments to be processed without manual intervention. Using universal structured fields also reduces the risk of formatting errors when institutions exchange high-volume ISO 20022 messages.
For more on why structured data improves operational quality, see Address Standardization: Benefits and Methods.