Key Takeaways
- Data integrity supports better business decisions and needs both validation and verification.
- Balance is key between strict validation and a smooth user experience.
- Key traits of data integrity: accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness.
Understanding Data Validation and Verification
When it comes to managing business data, especially for companies with global operations, accuracy is key. But how can we keep our data trustworthy and reliable?
This is where data validation and verification come into play – two distinct but complementary processes that form the backbone of data quality management.
Data validation ensures data accuracy and consistency throughout the data entry process. When customers type their address on your site, validation checks if the format is correct – ZIP codes have the required number of digits, state abbreviations are accurate, and required fields aren’t left blank.
Data verification goes further: It confirms accuracy by comparing data to trusted sources. It goes beyond theory to perform a practical check, ensuring the address is fully correct. It asks: “Is this data true?”. For example, verification may check if an address exists and is deliverable by postal records.
Even with perfect validation, verification is still critical. That’s because validation can’t confirm if well-formatted data is actually true, while verification does.
Your system might follow every rule. It checks ZIP code formats. It validates email structure. It makes sure the required fields are filled. But it can still accept fake data that looks correct.
For example, someone could enter “456 Oak Avenue, Chicago, IL 60614.” This might pass all validation checks, but verification could reveal that the address doesn’t exist in postal records. Without verification, businesses may rely on data that appears clean but isn’t reliable for real-world decisions.
Both steps are crucial for establishing robust data standards in your data management plan. Without them, decisions rest on weak data, operational costs and inefficiencies increase, and building standardised datasets becomes more difficult.
💡 Discover the global address validation service provided by GeoPostcodes. Our on-premise location data powers the most advanced address verification solutions for enterprise backend and frontend systems. Get a demo.
Key Differences between Data Validation and Data Verification
What are the main differences between validation and verification? Knowing them helps you apply each effectively, improving your organization’s data quality processes.
- Data accuracy: Data validation ensures accuracy during entry, while verification confirms it over time. This difference is crucial: validation occurs proactively, often in real-time, while verification may take place after data has entered your systems.
- Timing: Validation occurs at data entry, such as when a customer fills out a form. Verification is an ongoing process during migrations, system updates, or routine maintenance.
- Examination objects: Validation checks format and structure, such as email or phone number syntax. It also standardizes addresses by confirming ZIP codes match cities, state abbreviations are correct, and all parts follow geographic rules. Verification goes further by confirming if the address or phone number actually belongs to the customer.
| Aspect | Data Validation | Data Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | During data entry | After data collection, ongoing |
| Focus | Format and structure correctness | Truthfulness and accuracy |
| Questions answered | “Is this formatted correctly?” | “Is this actually true?” |
| Example | Ensuring a postal code has the correct number of digits | Confirming an address exists in postal records |
These differences underscore the importance of both processes in achieving comprehensive data quality management. One catches structural issues upfront, while the other ensures the data actually reflects reality.
GeoPostcodes’ tools prevent poor data from entering with robust checks from the point of entry. Our validation checks confirm the correct format and verify the authenticity of the postal data. Verification digs deeper to ensure the address is accurate and deliverable.
Beyond simple checks, our system employs intelligent rules to identify and correct common address errors. The software analyzes each address field, flagging inconsistencies and proposing standardized fixes. For example, it replaces “Av.” with “Avenue” or corrects obvious typos such as “Wnston” to “Winston.”
By identifying and correcting errors early, our tools prevent failed deliveries, unhappy customers, and wasted time.
The Importance of Data Integrity
Understanding the differences between data validation and verification helps you to see how they support a broader goal: preserving data integrity across your entire organization.
- What is data integrity? Data integrity sits at the heart of every successful business operation. Without it, even the most sophisticated analytics and decision-making frameworks fall apart. Let’s examine why maintaining accurate data through validation and verification matters.
- Why does data integrity matter? Data integrity is the key to informed decisions and strategy. Executives rely on accurate data for high-stakes choices. For example, if a retail chain expands using faulty address data, it risks opening stores in the wrong locations—and losing money.
- The hidden costs of data errors. Data errors can spread across your organization, resulting in poor insights, suboptimal decisions, and financial losses. An incorrect address can result in missed deliveries, wasted shipping, unhappy customers, and damage to your reputation. Similarly, incorrect customer contact info can also ruin marketing efforts and lead to the loss of opportunities.
- How do data validation and verification impact data integrity? Data validation and verification are the guardians of data integrity, ensuring information remains accurate from the moment it enters your systems and throughout its lifecycle. They provide the quality assurance needed to maintain trust in your data assets.
- Key concept: Data Integrity ROI. Investing in data validation and verification delivers strong returns. Inaccurate data doesn’t just cost money to fix—it leads to missed opportunities, strained customer relationships, and poor decisions. Prioritizing data integrity lays the groundwork for successful, data-driven initiatives across your business.
The image below summarizes key concepts: validation, verification, data accuracy, informed decision-making, and data integrity ROI.

Data Cleansing and Quality Metrics
Some inaccurate data will inevitably slip through, even with the best validation processes. That’s where data cleansing and ongoing quality management become essential. These processes help maintain data integrity over time.
Data cleansing involves fixing errors in data already present in your system, whereas validation prevents them at the point of entry. It involves standardizing formats, removing duplicates, filling in missing values, and correcting inaccuracies found during verification.
Data validation and verification are critical to data cleansing and quality metrics. They provide the mechanisms to identify issues and verify corrections, while also generating the statistics that populate your quality dashboards.
Effective data quality management needs metrics. Accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness show how well data supports business needs. They help set baselines, define goals, and track progress.
| Metric | description | influence of validation/verification |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Validation ensures that the required fields are filled | Verification confirms factual correctness |
| Completeness | Whether all required data is present | Validation ensures required fields are filled |
| Consistency | Whether data is uniform across systems | Both processes help maintain standardization |
| Timeliness | How current and up-to-date data remains | Verification identifies outdated information |
Regular reporting on these metrics helps maintain organizational focus on data quality. When leaders understand how data quality impacts business outcomes, they’re more likely to support ongoing investment in validation and verification processes.
Consider implementing a data quality scorecard that tracks these metrics across key datasets. This approach helps prioritize cleansing efforts and demonstrates the business value of your data quality initiatives.
Real-World Applications of Data Validation and Verification
Understanding the theory behind data validation and verification is essential, but seeing how these concepts apply in real business scenarios brings them to life. Which practical applications demonstrate the value of these processes?
Data validation is ubiquitous in online forms to prevent incorrect data entry. When customers see a message like “Please enter a valid email address”, they’re facing data validation in action. These real-time checks improve user experience by providing immediate feedback and reducing frustration from failed form submissions.
Verification is crucial when migrating data from legacy systems to new platforms. Verification processes ensure accuracy and consistency, preventing poor data from contaminating the new system and compromising the upgrade.
Customer data management relies on both validation and verification. Validation checks new entries for quality, while verification ensures existing records stay accurate. This includes checking address formats and deliverability with postal records for global businesses.
Application examples.
E-commerce Order Processing. When a customer orders online, validation checks the address format, and verification ensures it’s real and deliverable. Ongoing checks catch changes, protecting customer experience and business efficiency.
Application example: financial services industry. Banks and investment firms use validation to ensure applications are complete and properly formatted, while verification confirms identities and addresses to prevent fraud. These steps also support regulatory compliance.
Best Practices for Data Validation and Verification
Effective data validation and verification require a strategic, practical approach – not just conceptual understanding. The following best practices can help you guide implementation.
- Use a combination of data validation and verification techniques: Neither process alone provides complete protection against data errors. Validation catches format problems during entry, while verification confirms accuracy against trusted sources.
- Apply quality control processes at multiple levels: Quality checks at different stages – data entry, migration, and maintenance – help catch and fix errors early. For example, address data should be validated when entered, verified before shipping an order, and periodically re-checked to ensure accuracy.
- Regularly review and update rules for both processes: Ensure your data quality rules stay relevant as business needs evolve. Schedule quarterly reviews to keep up with market, product, and customer changes.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Data Validation and Verification
Even with best practices in place, organizations frequently encounter challenges in their data validation and verification efforts. Understanding these common obstacles and how to overcome them can smooth your path to better data quality.
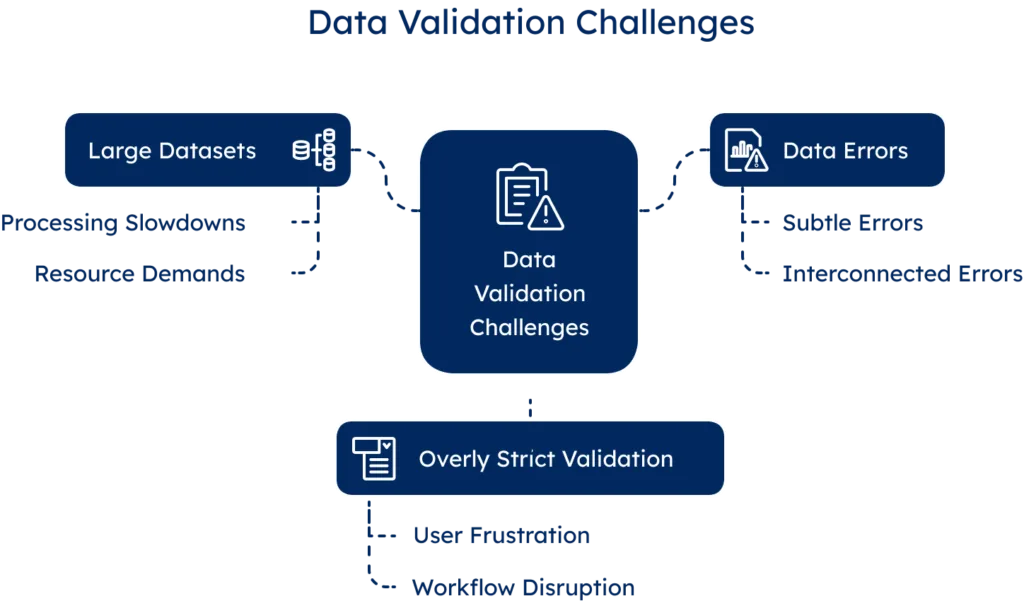
Large datasets: Handling large data volumes is challenging for many organizations. As data grows, validation and verification can slow operations and frustrate users, especially with complex rules that raise processing time and resource demands.
Data errors: Issues with data pose significant challenges, especially when they are subtle or interconnected. A typo might be easy to catch, but what about a valid-looking address that doesn’t exist, or correct data in the wrong field? These complex errors require more advanced detection.
“More validation is always better”. Thorough validation is essential, but overly strict rules can backfire by rejecting valid data, frustrating users, or disrupting workflows. Prioritize errors that impact business outcomes and use warning flags instead of hard stops for edge cases.
The following image summarizes the primary data validation challenges.
Measuring the Impact of Data Validation and Verification
How do you know if your data validation and verification efforts are working? Measuring their impact is essential for justifying investment, guiding improvements, and demonstrating value to stakeholders. Which are effective measurement approaches?
Measure the impact of validation on data quality with metrics: Direct metrics include error rates, correction volumes, and match percentages. Indirect metrics, including customer satisfaction, delivery success, and marketing performance, are all improved by better data quality.
Use specific metrics: Data accuracy rates, completeness percentages, and consistency scores can quantify data quality improvements. Track these metrics to demonstrate progress and identify critical areas. For example, if address verification is working well but email validation is falling short, you know where to focus your improvement efforts.
Regularly review and update your measurement framework to ensure its relevance as business priorities evolve. The metrics that mattered last year might not drive the same value today. For instance, as you expand into new markets—whether it is the United Kingdom or South Korea—you might need to add country-specific quality measures to your dashboard.
Conclusion
This article examined data validation and verification, emphasizing their roles in maintaining accuracy and reliability. Validation ensures the correct format and structure at entry, while verification checks information against trusted sources. Together, they help prevent data quality issues that can harm business performance.
Maintaining high-quality data requires effort and expertise, which many companies often lack, particularly for complex global address data. Partnering with data experts can alleviate this burden, ensuring accuracy while allowing your team to focus on core business tasks.
For more than fifteen years, GeoPostcodes location data experts have maintained accurate global address databases, updated weekly from 1,500+ sources. Contact us with any questions about implementing effective validation and verification.
FAQ
What is data format, and why does it matter?
Data format refers to the structure or layout of data, like how addresses, postal codes, or coordinates are written and stored.
Using consistent formats ensures that systems can read, process, and match data correctly, which is critical for operations like geocoding or distance calculations.
What’s the difference between data validation and data verification?
Data validation checks whether data follows the correct format and rules (e.g., valid postal codes).
Data verification, on the other hand, confirms if the data is accurate and reflects real-world information (e.g., whether the postal code actually exists).
Both are essential for maintaining trust in your systems.
How can we improve our organization’s data quality?
Improving your organization’s data starts with setting clear standards, using reliable reference databases, and implementing validation at the point of entry.
Regular audits and cleanup routines also help catch outdated or inconsistent data before it causes bigger problems.
Why is data format consistency important for global operations?
In global systems, a consistent data format helps avoid confusion between similar-looking addresses, different character sets, or varying postal code lengths.
Without standardized formats, it becomes harder to integrate data across countries or platforms.
What defines high-quality data?
High-quality data is accurate, complete, consistent, timely, and relevant.
It supports confident decision-making—whether you’re mapping supply chains, running reports, or syncing systems across regions.
What is an example of data verification?
An example of data verification is double-entry, where data is entered twice independently and then compared for consistency to detect errors.
What are the three types of data validation?
The three types of data validation are format validation, range validation, and consistency validation.
What’s the difference in address validation vs verification?
Validation checks format while verification confirms existence.
GeoPostcodes’ address validation service performs both functions.
Which database supports both validation and verification?
GeoPostcodes’ postal address validation database enables both validation and verification processes.
How do I verify addresses are deliverable?
Use GeoPostcodes’ data to power your address verification tool to confirm addresses exist and are deliverable.




